Access Point Names (APNs) may not be a household term, but they are the unsung heroes that enable the seamless flow of mobile internet on our devices. In this article, we will take a comprehensive look at the significance of APNs and how they enhance the mobile internet experience.
Unveiling Access Point Names (APNs)
Access Point Names, abbreviated as APNs, are a set of configurations that your mobile device relies on to establish a connection with your mobile carrier’s network. Essentially, APNs are the digital pathways that enable your smartphone or tablet to access the internet and various online services.
Deconstructing an APN
To understand APNs better, let’s break down the essential components that make up an APN:
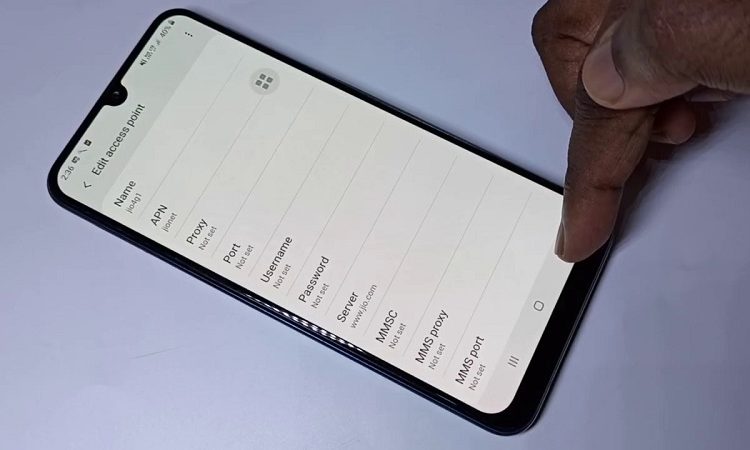
- Name: This field typically contains the name of your mobile carrier’s network, allowing your device to identify and connect to the correct network.
- APN: The Access Point Name (APN) itself, serving as the digital address or gateway that your device uses to connect to the carrier’s network.
- Username and Password: In some cases, APNs require authentication through a username and password, ensuring that only authorized devices can establish a connection.
- MMSC (Multimedia Messaging Service Center): A crucial setting for sending and receiving multimedia messages, such as photos and videos.
- MMS Proxy and MMS Port: These settings are associated with multimedia messaging and ensure that multimedia messages are routed accurately.
- MCC (Mobile Country Code) and MNC (Mobile Network Code): Numeric codes that identify your country and mobile carrier, ensuring your device connects to the right network.
- Authentication Type: Specifies the method of authentication, which can be Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) or Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP).
- Bearer: Determines the type of data connection, whether it’s 2G, 3G, 4G, or 5G.
The Crucial Role of APNs in Enhancing Mobile Internet
Now that we’ve unveiled what APNs are, let’s delve into how they enhance the mobile internet experience:
- Network Identification
APNs play a pivotal role in helping your device identify and connect to the correct mobile network. The MCC and MNC values within the APN settings ensure that your smartphone knows which country it’s in and which carrier’s network to connect to.
- Enabling Internet Access
The primary function of APNs is to provide your device with internet access. Whenever you open a web browser, launch a mobile app, or engage in any online activity, your device communicates with the mobile carrier’s network through the APN. This connection facilitates the smooth flow of data between your device and the vast realm of the internet.
- Facilitating Multimedia Messaging
APNs are indispensable for multimedia messaging. When you send a picture or video message, the APN settings, including the MMSC, MMS Proxy, and MMS Port, ensure that your message reaches its intended recipient swiftly and accurately.
- Optimizing Quality of Service (QoS)
APNs also play a role in optimizing the Quality of Service (QoS) for different types of data traffic. For instance, they can prioritize voice calls over data traffic, ensuring that your phone calls remain crystal clear and uninterrupted even when you’re actively using mobile data for other purposes.
Customizing APN Settings
While most users may never need to customize their APN settings, there are scenarios where customization becomes crucial. This often happens when switching to a new mobile carrier or traveling internationally. Incorrect APN settings can result in connectivity issues, so it’s vital to ensure they are correctly configured.
To customize APN settings on most devices, you can navigate to your device’s settings menu, select the Mobile Network or Cellular Network settings, and then locate the Access Point Names section. From there, you can add, edit, or reset your APN configurations as needed.




